Indian scientist discovered burning gas around the Milky Way
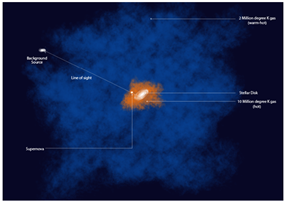
The veil, identified primarily through advanced imaging techniques, consists of ionized gas and hot plasma, extending far beyond the visible components of the galaxy. This gaseous halo plays a crucial role in various astronomical processes, including star formation and the interplay of dark matter. The composition of this gas, largely consisting of hydrogen and helium, indicates ongoing and unresolved dynamics within our galaxy that are critical for understanding its life cycle.
Additionally, the presence of this fiery veil signifies interactions between the Milky Way and its extragalactic environment, highlighting the importance of gravitational and electromagnetic forces in shaping galactic structures. It serves as a conduit for the exchange of materials, energies, and even gases between neighboring galaxies, thus underpinning a cosmic network that extends across the universe.
In conclusion, the revelation of the veil of fiery gas surrounding the Milky Way disc provides invaluable insights into the complexity of our galaxy. As researchers continue to explore and interpret these findings, it will pave the way for a more comprehensive understanding of the cosmic phenomena that define our universe. Further investigation into this gas veil may illuminate the mysteries of galactic formation and evolution, enriching our knowledge of celestial mechanics and the broader cosmos.
